Macos Ubuntu Vm
Windows, macOS – which one do you want to use today? On a traditional setup, you’re stuck with one or the other. But with virtual box, you actually have macOS on a Windows PC.
It’s the freedom that computer users have enjoyed with Linux and other operating systems.
But Apple has made it difficult to install their operating system on anything other than their own hardware. All of that is changing, and Virtual Box is responsible for it and the rise of the Hackintosh.
New to hackintosh? Learn more about it in our what is hackintosh? overview.
Note: A lot of people will be able to get a mac virtual machine one Windows running smoothly, but sound doesn’t seem to work well. That’s really not an issue because you’ll still be able to access all of your apps and software.
I also recommend that you have access to a real Mac. You might be able to find some distributions of the High Sierra ISO online, but there is always a risk when downloading from an unofficial source. Instead, borrow a Mac from a friend, or use your own and download the High Sierra OS from the App Store.
Check out our high sierra installation guide for hackintosh
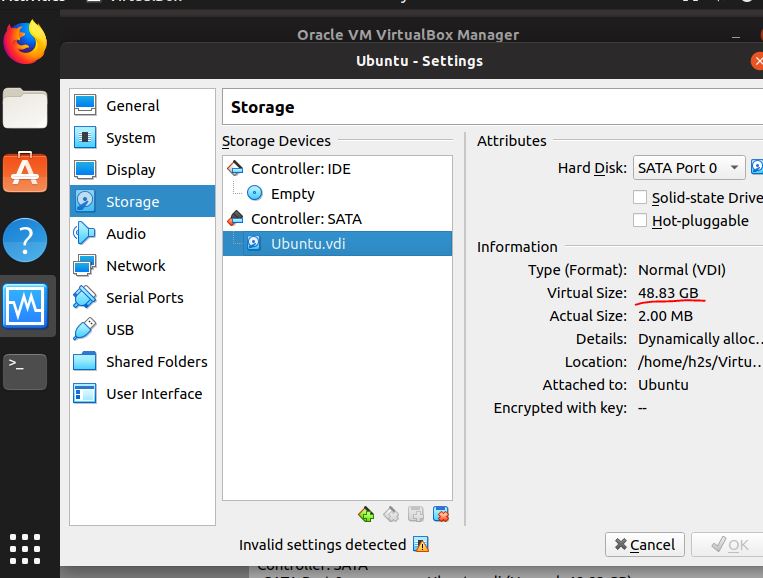
A simple macOS VM in QEMU, accelerated by KVM Obviously we are talking about a simple procedure that implies the use of huge hardware resources: already a Mac in itself uses powerful hardware let alone virtualize it what computing power we need. The drawback is that macOS will have less to use while Ubuntu is running. At a minimum, give Ubuntu at 1GB (1024MB) of RAM. When you’ve decided how much memory (RAM) to give Ubuntu, click the Continue button. On the Hard drive screen, select Create a virtual hard drive now and then click Create. Notice: There is now an official release of checkra1n for linux! This method is outdated!New guide: #Checkra1n #Tutorial #. I have an ubuntu VM running in VirtualBox. I am trying to ping it, but cannot. I have the network setting changed from 'NAT' to 'bridged'. Here is the screenshot of the ip address info: and here. Create a virtual machine to install Ubuntu This guide explains how to use a virtual machine (VM), a software environment that an operating system sees as a physical PC, to run Ubuntu. It doesn't matter what operating system you have installed on your PC (referred to as the 'host'), one or more can be installed in a virtual machine.
Macos Vm On Macos
Everything You Need to Get Started with Installing macOS on VirtualBox
Before we go through the steps on how to install macOS on Virtual Box, let’s get everything together that you’ll need to get started.
- Open up your Mac
- Go to the App Store
- Type in “High Sierra”
You’ll want to search for your desired operating system (we’ll be using High Sierra), and Download it.
Note: You’ll need a decent computer to be able to run Virtual Box. Your computer will need to meet these minimum requirements:
- Dual core processor
- 4GB Ram or higher
- 64-bit
If your computer doesn’t meet these requirements, you won’t be able to run macOS properly. You’ll be able to download VirtualBox from the official website. I’m not going to go through the installation process, as the website will have all of the information you need to be able to install VirtualBox.
I do recommend that you read all of the documentation and ask any questions that you have in the community section of the website.
VirtualBox 6.0 was just released, so it’s definitely a great time to get started with your own macOS.
Extract macOS Sierra
Make sure you’ve downloaded High Sierra, and then you’ll want to run a few commands from your terminal . You’ll be able to open the terminal at: Applications > Utilities > Terminal. Once inside of the terminal, you’ll want to run the following commands:
Go to your desktop and rename the file, removing the “.cdr” extension. You need this extension to read “.iso” for it to work properly.
You’ve successfully created your own ISO file so that you can bootup your macOS.
The next step is to copy the file over to your Windows machine (using a large USB drive seems to work best). This file will be mounted in your virtual machine later on in the article, so it’s very important that this step is completed successfully.
Creating a mac Virtual Machine on Windows
You’ll want to create a virtual machine, and this is really easy. You’ll open up VirtualBox and click New. You’ll want to have the following parameters selected or entered before clicking Next.
- Name: High Sierra
- Type: Mac OS X
- Version: Mac OS X (64-bit)
Pay attention when selecting the version because you may find that High Sierra is offered as a version when you go to install it. But if it’s not, you can just choose the settings I listed above and they should work fine.
You’ll then be proceeding through all of the settings.
When you come up to the RAM setting, you’ll want to be generous. VirtualBox requires a minimum of 4GB or RAM to run, but the more the better.
Why?
You’ll want to provide at least 4GB to your macOS, or 4096MB to be precise. A general rule of thumb is that if you can spare it, supply more RAM to your virtual machine. RAM will allow the operating system to put more information into memory and retrieve it faster.
For better overall performance, supply as much RAM as you can.
The next steps are also important, and they’ll include:

- Hard Disk: Choose the “Create a virtual hard disk now” setting.
- Choose VDI when choosing the hard disk type.
- Choose Fixed Size instead of Dynamic for added speed.
- Set the size of the drive to at least 25GB.
You’ll now have your virtual machine using the RAM and disk space properly, and you’ll have to work your way through a few screen prompts before having everything setup properly.
Configuring Your VirtualBox to Run macOS High Sierra
We’ve made a lot of progress so far, and now it’s time to configure your virtual machine properly. You’ll see in the main window of VirtualBox that “High Sierra” is listed. Click on this and then click on the “Settings” button.
You’ll want to go to “System” and make sure that the following are unchecked on the Motherboard tab:
- Floppy
- Network
Click on the Processor tab and make sure that you have 2 or more CPUs set for your virtual machine.
The next few settings are rather simple:
- Display: Video Memory with a minimum of 128MB
- Storage: Click “Empty” and then click on the CD at the top right. Choose your High Sierra ISO file
Now you’ll need to click “Ok,” and save all of the changes you’ve made. Close out your VirtualBox now.
Apple is very strict on the system that their operating system runs on, so it’s very important that you do your best to configure your virtual machine in such a way that it tricks the installer to thinking you’re on a retail machine.
We’ll now be going into the Windowscommand prompt.
You’ll do this by:
- Clicking the Start Menu
- Typing “Command Prompt”
- Right-clicking on the Command Prompt desktop app
- Choosing Run as administrator
It’s very important to follow all of the following command prompts exactly. Your goal is to run each command, one by one, hitting the Enter button and waiting for the command to complete successfully.
Remember that VirtualBox needs to be closed before running these commands, or it won’t work properly.
You have to make sure that the virtual machine is properly named “High Sierra” for this method to work. If not, you’ll be able to go back and make changes to the name to get everything to work properly.
Once all of the commands are completed, and there are no errors, you’ll then be able to open up your VirtualBox and get macOS High Sierra installed properly on VirtualBox.
It’s a long process, but we’re almost done with your installation.
Running VirtualBox and the macOS Installer
You’ve almost learned how to install macOS on VirtualBox entirely, and we’re on the home stretch. You’ll want to open up your VirtualBox and then click on your virtual machine that you set up earlier.
Now, click “Start.”
There will be a lot of information displayed on the screen as everything starts running. I recommend stepping away from the machine and letting it run for a few minutes before coming back. Some errors can hang for 5 minutes or longer.
If you’ve done everything properly, you can be confident that the installer will boot properly.
You’ll eventually be presented with the option to pick a Language. If you’ve reached this point, you’re doing very well and are almost ready to run your macOS.
The next steps can be followed:
- Choose your desired language, and click
- Click “Disk Utility” and then
- Click “View” and then “Show All Devices.”
- Click on your empty virtual drive that has been setup and click “Erase.”
- Choose the following settings:
- Name: Macintosh HD
- Format: Mac OS Extended (Journaled)
- Scheme: GUID Partition Map
- Click “Erase” and close Disk Utility when the process is complete.
- Click “Reinstall macOS.”
- Click “Continue.”
You’ll come up to one point where you’ll be asked to choose a hard drive, and you’ll want to select the Macintosh HD partition that you just created with the Disk Utility.
We’ve successfully copied all of the files on the virtual machine, but we’re not done just yet.
Exit your virtual machine and then go back to your virtual machine’s settings. You’ll need to change up your Storage settings. Click on your ISO for High Sierra in the “Storage Tree.” You’ll click that CD icon just like we did earlier and then choose “Remove Disk from Virtual Disk.”
You need to do this to unlink the ISO from your virtual machine.
Start up your virtual machine and you should come across a black screen with the EFI Internal Shell. You’ll want to look for FS1. If this is listed in yellow, click on the virtual machine and then type fs1: and hit the Enter button.
You should be in the fs1 directory.
Type in the following commands:
- cd “macOS Install Data”
- cd “Locked Files”
- cd “Boot Files”
Now we’ll run the installer by running: boot.efi and hitting enter.
If everything goes well, you’ll come across a graphical installer and will just have to work through the prompts. The virtual machine will reboot eventually and then you’ll need to go through the settings and the rest of the setup process.
Soon enough, you’ll be right inside of macOS, where you’ll be able to start using your mac virtual machine on Windows.
Having a virtualbox mac OS is the easiest method of using mac as and when you need it. In addition, using virtualbox is far less complicated than the dual boot hackintosh method we have looked at previously.
Jan 15, 2015
Buy VMWare Fusion, download, andinstall (write the serial number during installation). To get quicklystarted, you download a trial version for free and later buy it andregister the serial number (easy).
Go tohttp://www.ubuntu.com/desktop/get-ubuntu/downloadand choose the latest 64-bit Desktop version of Ubuntu.Save the downloaded Ubuntufile at some place you can recognize later.
Other Linux distributions.We strongly recommend to use a Debian-based GNU/Linux distribution,because Debian has by far the largest collection of prebuiltmathematical software.Among the Debian-based distributions, we recommend Ubuntu, simply becauseswitching keyboard layouts is more reliable or easier in Ubuntu than in, e.g.,Lubuntu, Xubuntu, and Linux Mint (a configured layout might be goneafter a reboot). Switching keyboard layouts are particularlyconvenient when doing programming with an English/American keyboard,with braces and brackets in natural places,and then writing emails using a native keyboard with special characters.
- Launch VMWare Fusion (the instructions here are for version 7).
- Click on File - New and choose to Install from disc or image.
- Click on Use another disc or disc image and choose your
.isofile with the Ubuntu image. - Choose Easy Install, fill in password, and check the box for sharing files with the host operating system.
- Choose Customize Settings and make the following settings (these settings can be changed later, if desired):
- Processors and Memory: Set a minimum of 2 Gb memory, but not more than half of your computer's total memory. The virtual machine can use all processors.
- Hard Disk: Choose how much disk space you want to use inside the virtual machine (20 Gb is considered a minimum).
- Choose where you want to store virtual machine files on the hard disk. The default location is usually fine. The directory with the virtual machine files needs to be frequently backed up so make sure you know where it is.
- Ubuntu will now install itself without further dialog, but it will take some time.
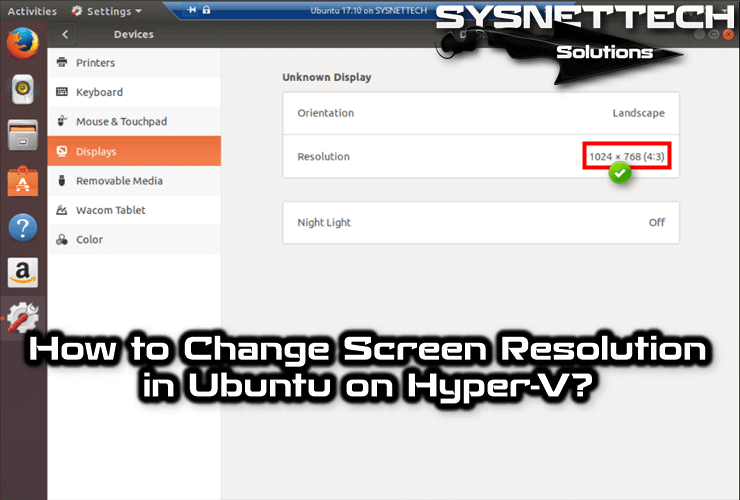
- You may need to define a higher resolution of the display in the Ubuntu machine. Find the System settings icon on the left, go to Display, choose some display (you can try several, click Keep this configuration when you are satisfied).
- You can have multiple keyboards on Ubuntu. Launch System settings, go to Keyboard, click the Text entry hyperlink, add keyboard(s) (Input sources to use), and choose a shortcut, say
Ctrl+spaceorCtrl+backslash, in the Switch to next source using field. Then you can use the shortcut to quickly switch keyboard. - A terminal window is key for programmers. Click on the Ubuntu icon on the top of the left pane, search for
gnome-terminal, right-click its new icon in the left pane and chooseLock to Launchersuch that you always have the terminal easily accessible when you log in. Thegnome-terminalcan have multiple tabs (Ctrl+shift+tto make a new tab).
Installing software on Ubuntu
You now have a full Ubuntu machine, but there is not much softwareon a it. Installation is performed through the Ubuntu Software Center (agraphical application) or through Unix commands, typically
To look up the right package name, run apt-cache search followed bytypical words of that package. The strength of the apt-get wayof installing software is that the package and all packages it depends onare automatically installed through the apt-get install command.This is in a nutshell why Ubuntu (or Debian-based Linux systems)are so user-friendly for installing sophisticated mathematical software.
To install a lot of useful packages for scientific work, go tohttp://goo.gl/RVHixr and click on one of the followingfiles, which will install a collection of software for scientific workusing apt-get:
install_minimal.sh: install a minimal collection (recommended)install_rich.sh: install a rich collection (takes time to run)
The program will run for quite some time, hopefully without problems.If it stops, set a comment sign # in front of the line where it stoppedand rerun.
File sharing
The Ubuntu machine can see the files on your host system if youdownload VMWare Tools. Go to the Virtual Machine pull-down menu inVMWare Fusion and choose Install VMWare Tools. A tarfile isdownloaded. Click on it and it will open a folder vmware-tools-distrib,normally in your home folder. Move to the new folder andrun sudo perl vmware-install.pl.You can go with the default answers to all the questions.
On a Mac, you must open Virtual Machine - Settings... and chooseSharing to bring up a dialog where you can add the folders you wantto be visible in Ubuntu. Just choose your home folder. Then turn onthe file sharing button (or turn off and on again). Go to Ubuntu andcheck if you can see all your host system's files in /mnt/hgfs/.
If you later detect that /mnt/hgfs/ folder has become empty,VMWare Tools must be reinstalled by runningsudo perl vmware-install.pl as above or

Documents/Virtual Machines/Ubuntu 64-bitMacos Catalina Ubuntu Vmware
.Backing up the Ubuntu machine means backing up this folder.However, if you use tools like Time Machine and work in Ubuntu duringbackup, the copy of the state of the Ubuntu machine is likely tobe corrupt. You are therefore strongly recommended to shut down thevirtual machine prior to running Time Machine or simply copying thefolder with the virtual machine to some backup disk.If something happens to your virtual machine, it is usually a straightforwardtask to make a new machine and import data and software automaticallyfrom the previous machine.
Macos Ubuntu Vmware
Internet Does not Work in Ubuntu.Invoke the VMWare Fusion menu Virtual Machine - Settings - Networkand test Share the Mac's network connection versus Connect directly tothe physical network (Bridged).
